The human population has experienced exponential growth in the last three centuries. In just the past 100 years, we've seen an additional 6 billion people, bringing the total population to over 8 billion. This rapid growth has significant implications for resource management, sustainability, and infrastructure needs.
By 2050, nearly 10 billion people will live on the planet. Can we produce enough food sustainably?
The ever-expanding human population casts a long shadow over the future of our planet and ourselves. As populations surge, particularly in developing nations, many challenges threaten the foundations of our existence. This surge in human numbers translates into an ever-increasing demand for resources, pushing the limits of our planet's capacity and jeopardizing long-term sustainability.
Food for All, or Food for Some?
Feeding a growing population is a monumental task. Increased food production puts immense pressure on agricultural lands, leading to:
- Water Scarcity: Expanding irrigation depletes freshwater reserves, jeopardizing ecosystems and human needs.
- Environmental Degradation: Intensive farming practices lead to deforestation, soil erosion, and a decline in soil fertility, negatively impacting future harvests.
- Pollution: Increased use of fertilizers and pesticides contaminates water sources and harms biodiversity.
Limited Resources, Unequal Distribution:
The Earth's resources are finite, and competition intensifies as populations grow. Concerns like:
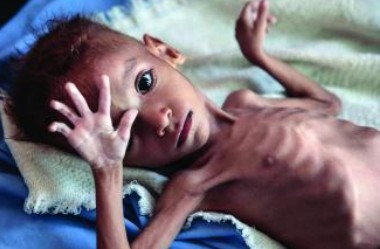
- Inequality: Not everyone benefits equally from available resources. Food insecurity and malnutrition could worsen for vulnerable populations.
- Biodiversity Loss: Habitat destruction for agriculture disrupts ecosystems, endangering species and jeopardizing ecological balance.
Climate Change: A Looming Crisis
The rise in global population directly contributes to:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Increased energy consumption and industrial activity linked to food production and resource extraction propel climate change.
- Global Warming: Rising temperatures threaten food security, exacerbate extreme weather events, and disrupt weather patterns.
Geopolitical Tensions on the Rise
Competition for dwindling resources like water and arable land can lead to:
- Political Conflict: Disputes over resource allocation and environmental concerns could escalate into international tensions.
- Mass Migration: Climate change and environmental degradation could displace populations, triggering large-scale migration and humanitarian crises.
The global population boom presents a complex and multifaceted challenge. The strain on resources, the acceleration of climate change, and the potential for political instability paint a worrying picture for the future. Humanity's future remains uncertain without significant changes in consumption patterns, resource management, and technological innovations.
Changing Consumption Habits
-
Shift towards Protein-Rich Diets: As incomes rise, there is often a shift towards diets that include more protein, particularly from animal sources. This trend puts additional pressure on food systems as animal agriculture generally requires more resources than plant-based protein sources.
-
Demand for Processed Foods: With urbanization and changing lifestyles, there is a growing demand for processed and convenience foods. The production and processing of these foods often involve high energy inputs and contribute to environmental pollution.
-
Resource-Intensive Foods: Certain foods, such as red meat, dairy products, and exotic fruits, require more resources like land, water, and energy for production. Meeting the increasing demand for these resource-intensive foods can strain natural resources and contribute to environmental degradation.
-
Food Waste: Alongside increased demand, changing consumption habits also lead to higher levels of food waste. Food wastage at the consumer level exacerbates food insecurity by limiting food availability for those in need.
-
Nutritional Transition: As populations become more affluent, there is a transition towards diets high in processed foods, sugars, and fats, which can have negative implications for public health, leading to higher rates of diet-related diseases such as obesity and cardiovascular issues.
-
Cultural Influences: Globalization and urbanization can lead to adopting Western dietary habits in various regions. While this can offer diversity in food choices, it may also introduce unsustainable food consumption patterns that strain local resources.
-
Demand for Variety: Consumers increasingly seek diverse and exotic foods that may not be locally available. Meeting this demand often involves long supply chains, increasing carbon emissions, and environmental impact.
Global Population Growth poses significant challenges to food security due to several interconnected factors
-
Increased Demand: As the global population grows, so does the demand for food, putting pressure on existing food production systems to produce more to meet the needs of a larger population.
-
Resource Scarcity: With more mouths to feed, there is an increased strain on natural resources such as arable land, water, and energy. A growing population requires more resources for food production, leading to potential scarcity and competition for these essential resources.
-
Limited Agricultural Land: The expanding population necessitates more agricultural land for food production. However, the availability of arable land is finite, and converting natural habitats into agricultural land can lead to environmental degradation, loss of biodiversity, and soil fertility issues.
-
Climate Change Impacts: Global Population Growth exacerbates climate change's impacts on food systems. Extreme weather events, shifting rainfall patterns, and temperature changes can affect agricultural productivity, leading to crop failures and food shortages.
-
Food Insecurity: A rapidly growing population can outpace food production, leading to insecurity in vulnerable regions. Inadequate access to nutritious food can harm public health, particularly in developing countries.
-
Distribution Challenges: As the population grows, equitable food distribution becomes more challenging. Disparities in food access and affordability can deepen, leading to issues of hunger and malnutrition, especially in underserved populations.
-
Pressure on Food Supply Chains: The increasing population pressures food supply chains to deliver food from producers to consumers efficiently. Any disruptions in these supply chains, whether due to natural disasters, conflicts, or other factors, can impact food availability and access.